
- Central Banks
- ECB
- Monetary Policy
ECB Holds Interest Rates at 2% as Inflation Hits Target
5 minute read

European Central Bank maintains steady borrowing costs as tech companies benefit from stable financing conditions in recovering eurozone
Key Takeaways
- ECB holds rates at 2% as inflation aligns with central bank’s target amid ongoing U.S. tariff uncertainty
- Eurozone growth projects 1.2% in 2025 revised up from June’s 0.9% forecast despite trade headwinds
- Tech companies maintain access to affordable capital supporting continued investment in R&D and AI development
Introduction
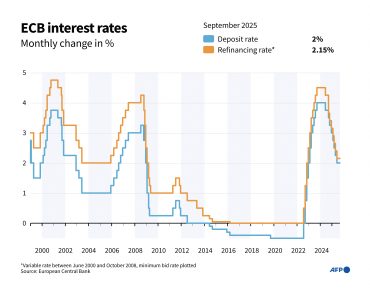
The European Central Bank maintained its benchmark interest rate at 2% this month, delivering the widely anticipated decision as inflation hovers near the central bank’s target. The rate hold affects the deposit facility rate, which banks receive for overnight deposits with the ECB, alongside unchanged rates for main refinancing operations at 2.15% and marginal lending facility at 2.40%.
Markets had priced in a 99% probability of the ECB keeping rates steady, reflecting confidence in the central bank’s data-driven approach amid persistent trade tensions with the United States. The decision carries significant implications for European businesses, particularly in the technology sector where access to capital remains crucial for innovation and expansion.
Key Developments
ECB President Christine Lagarde emphasized the central bank’s commitment to data-dependent policy decisions without providing clear forward guidance. “We are in a good place because inflation is at 2%,” Lagarde stated, noting that projections point to inflation stabilizing at target over the medium term.
The monetary policy stance reflects the ECB’s assessment of current economic conditions, including the impact of a recent transatlantic trade agreement imposing 15% tariffs on EU exports to the U.S. While some trade issues remain unresolved, particularly in wine and spirits, the agreement provides greater clarity for business planning.
Eurozone economic growth showed modest gains of 0.1% in the second quarter, down from the previous 0.6% expansion. The ECB revised its 2025 growth projection upward to 1.2% from June’s 0.9% forecast, while slightly lowering the 2026 outlook to 1.0%.
Market Impact
The rate decision reinforces stable financing conditions for European corporations, with the average interest rate on new business loans to firms continuing to decrease. Corporate bond issuance growth has accelerated, reflecting improved access to capital markets.
Technology companies across the eurozone benefit from continued access to relatively affordable capital, supporting ongoing investments in semiconductors, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence development. The stable borrowing environment enables firms to maintain flexible capital structures while conserving cash for potential policy shifts.
The unemployment rate remains low at 6.2%, supporting consumer spending and domestic demand resilience that contributed to 0.7% cumulative growth over the first half of the year.
Strategic Insights
The ECB’s cautious approach reflects broader structural challenges facing the eurozone economy, including persistent trade barriers driving regionalized supply chains and “friend-shoring” strategies. Technology firms are adapting by accelerating innovation efforts and building supply chain resilience to navigate ongoing tariff uncertainties.
Political turmoil in France, the EU’s second-largest economy, adds complexity to the investment environment, potentially constraining business expansion plans. This uncertainty encourages companies to prioritize operational flexibility and maintain strong balance sheets.
The stable monetary environment may reinforce regulatory pressure on tech firms to pursue energy-efficient innovations aligned with the EU’s green agenda, particularly in emerging fields like quantum computing and cybersecurity.

Expert Opinions and Data
Ángel Talavera, head of European macro at Oxford Economics, argues that the trade agreement “has reduced some of the worst tail risks and should lay the foundation for a moderate improvement in activity next year.” However, he cautions that weak growth in exports and investment will continue shaping the immediate outlook.
Oxford Economics expects the ECB to implement one additional rate cut in December, though analysts note “there is a reasonable chance it will stay put.” According to CNBC, this reflects the central bank’s careful balance between supporting growth and maintaining price stability.
Irene Lauro of Schroders suggests that trade uncertainty is decreasing and an end to the easing cycle approaches, supported by strengthening labor markets and domestic demand. The ECB projects headline inflation to average 2.1% in 2025, with core inflation expected at 2.4% before declining to 1.9% in 2026.
Conclusion
The ECB’s rate hold provides immediate stability for European businesses while maintaining policy flexibility to address evolving economic conditions. Technology companies gain continued access to affordable financing, supporting strategic investments in innovation and expansion.
The central bank’s data-dependent approach signals ongoing vigilance regarding inflation trends and trade policy developments. Current monetary conditions support economic activity through improved financing terms, though persistent uncertainties require businesses to maintain adaptive strategies focused on resilience and operational efficiency.








